When it comes to the performance of memory, the “read speed” and “latency” of the memory module come directly to mind. Generally, on the product specification table is actually the value of “frequency” and “timing”. This is known as conversion and does not directly mean that the two values are equal. If you ask me which value is more important, I would say~~ both! (Don’t roll your eyes at me, read on and you will understand why!)


CL: Short for CAS latency, refers to how long the computer needs to wait before it can actually start reading data from memory. Therefore, for two memory modules with the same frequency, a higher CL means a longer delay time. It is worth noting that the unit of CL is not minutes or seconds, but represents clock cycles, which is a variable in the formula for calculating memory delay time. Taking the specification of T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5 as an example, the total number of clock cycles of DDR5-6000 CL38 is equal to 38. Are you running out of memory in your head after reading everything above? Don’t worry, I’ll show you how to figure out the latency of the memory module in seconds with a calculator by looking at the DRAM specification table!

The unit of latency time is expressed in nanoseconds (ns), and the formula is as follows:

According to the above formula, we’ll give two examples to explain to you:
[Example 1]
At the same frequency, the effect of different CLs on the latency time.
Calculation based on the two specifications of T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-6000 CL30 and T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-6000 CL38
T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-6000 CL30
Latency time (ns) = 30 x [1000 ÷ (6000 ÷ 2)] ≒ 9.99 ns
T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-6000 CL38
Latency time (ns) = 38 x [1000 ÷ (6000 ÷ 2)] ≒ 12.66 ns
When the memory frequency is the same, the lower the CL, the shorter the latency time will be, and the less time the computer has to wait to read the memory data, which means the better the performance.
[Example 2]
Under the same CL, the effect of different frequencies on the latency time.
Calculation based on the two specifications of T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-5600 CL40 and T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-6400 CL40
T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-5600 CL40
Latency time (ns) = 40 x [1000 ÷ (5600 ÷ 2)] ≒ 14.29 ns
T-FORCE DELTA RGB DDR5-6400 CL40
Latency time (ns) = 40 x [1000 ÷ (6400 ÷ 2)] = 12.5 ns
When the memory CL is the same, the higher the frequency, the shorter the latency, and the shorter the time the computer has to wait to read the memory data, which means the better the performance.
※The latency time calculated by the above formula is a theoretical value※

After the mind-twisting calculation, let’s return to the title of this article. Is CL the lower the better in performance of memory module? I think there’s no definitive answer! Like we said at the beginning, the performance of the memory is also affected by the frequency and timing, so the CL in the memory cannot be used to define the performance of memory alone.
4. How to pick a suitable memory?
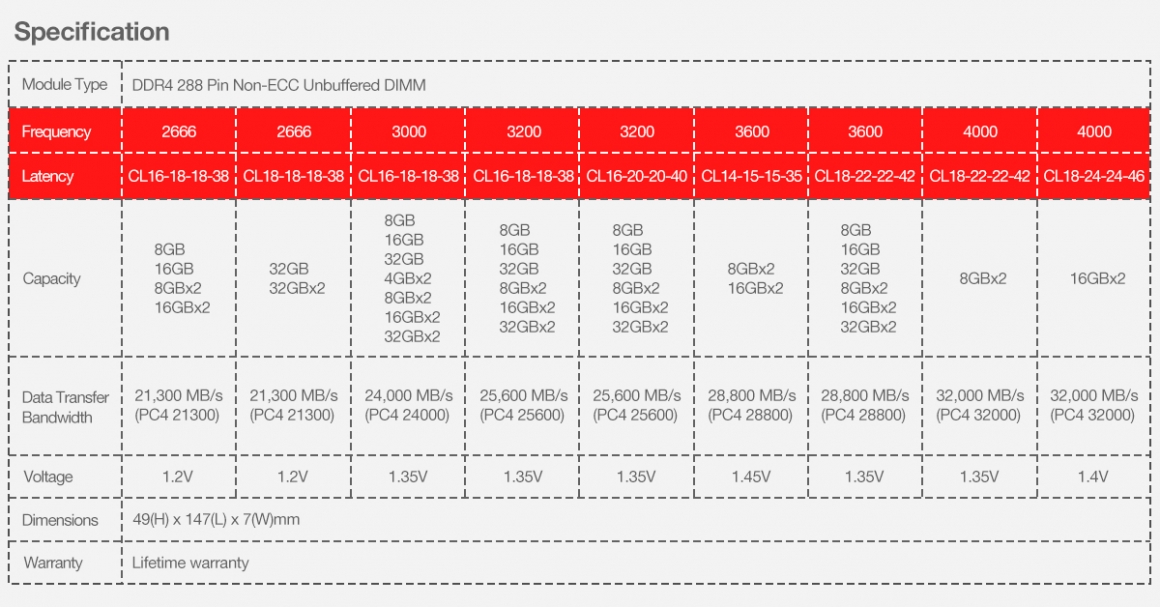
When buying memory, you should consider factors such as capacity, frequency, CL, etc. The most important thing is the compatibility with the motherboard and CPU. I suggest you decide the size of memory and frequency first, and then choose the size of the CL. Usually, the price is higher if the performance of the memory module is better. Once you’ve decided on the memory specification, remember to make sure it’s compatible with your motherboard or CPU!
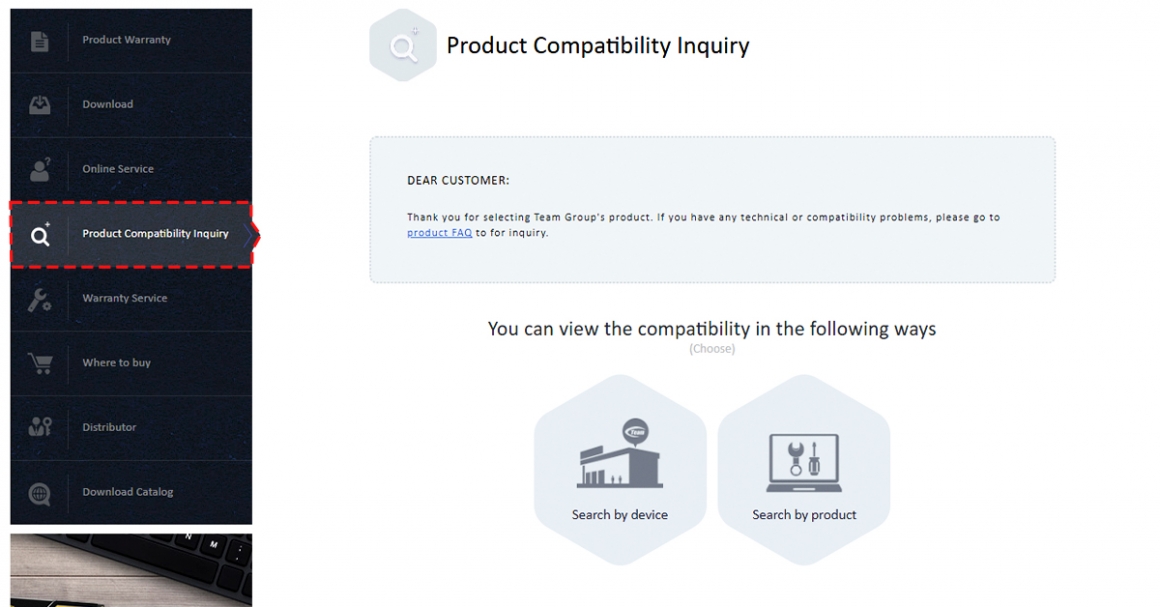
The compatibility of TEAMGROUP’s memory modules can be confirmed through TEAMGROUP’s Product Compatibility Inquiry page. If you have any questions about TEAMGROUP’s products, please leave a message below or visit TEAMGROUP’s Online Service page for inquiry!
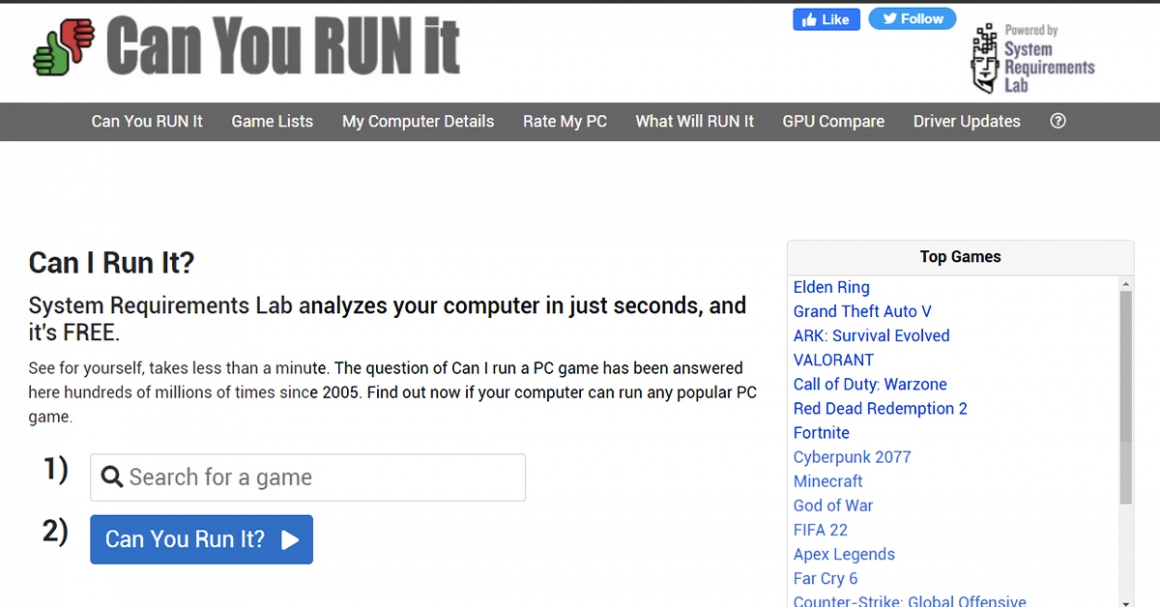
If you like to choose and upgrade your own computer parts and enjoy the fun of installing them, but are not sure whether the specifications support the new 3A games, you can go to the Can You Run It website for reference. Enter the game you want to search in the “1)” search bar. Press “2)” Can You Run It? It will jump to the result page, and the result can be used as a reference for options or upgrades.
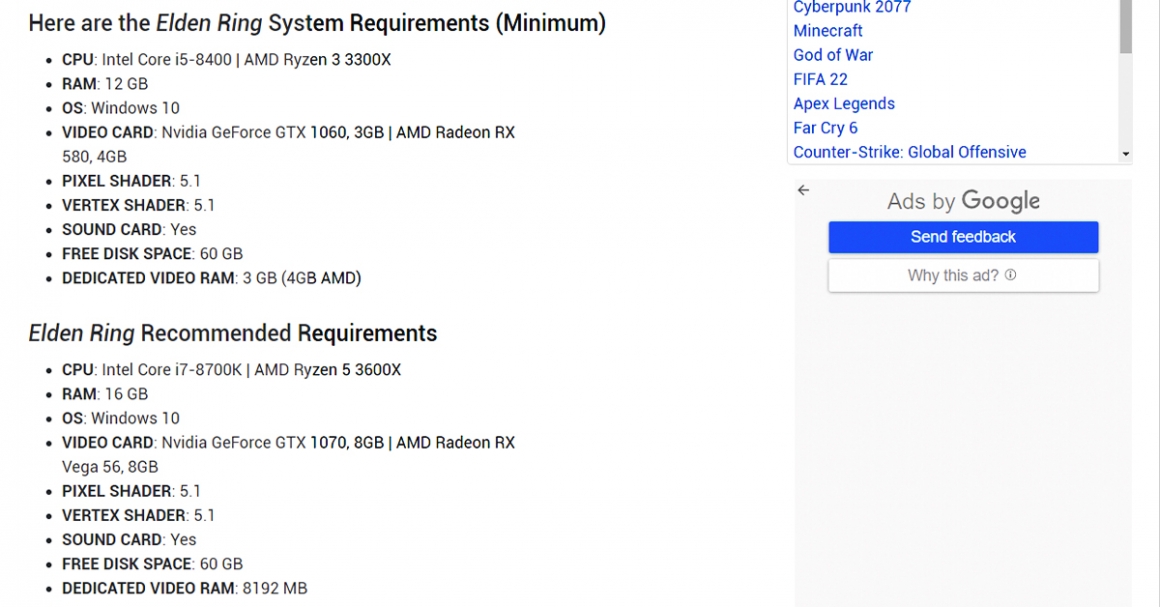
If you want to know if memory at different frequencies and capacities will affect the FPS of the game, I’ve put together links for you below, go check it out!
https://www.teamgroupinc.com/en/blogs/ram-frequency-fps-II-en