
When upgrading SSD, besides reading and writing speed, another key point is the storage capacity! But I guess you T-fans will also look at the price and determine if it is good value (After all, it’s our hard-earned money). However, let’s not discuss the price today. Do you know that high-capacity SSDs actually have more advantages than you can imagine? I will briefly introduce you to familiar strangers such as “Wear Leveling, TBW and SLC Cache”, so you will definitely want to buy a high-capacity SSD after reading this!
1. Wear Leveling
Wear Leveling technology is used to write data evenly into the storage blocks of the SSD, thereby increasing the service life of the SSD.

The number of program/erase cycle of each storage block in SSD is fixed, if the number is exceeded, the block will be corrupted and will no longer be used. The “Wear Leveling” will give priority to writing data to blocks with a lower number of program/erase cycle, so that each block is used evenly. The larger the capacity of the SSD, the more blocks can be written to and erased, so each block is less likely to be written to and erased repeatedly, and therefore less likely to be damaged, which increases the durability and service life of the SSD.
2. TeraBytes Written (TBW)
According to JEDEC, the number of TBW (TeraBytes Written) indicates the total terabytes written in an SSD. Simply put, it is how many TBs of data can be written in the service life of the SSD. Take the
TEAMGROUP MP34 M.2 PCIe SSD 2TB for example, its TBW value is 2,000TBW, it means that the total amount of data that can be written in its service life is 2,000TB.

The larger the capacity of the SSD, the larger the TBW value, the more data can be written to the SSD, which indirectly means it can be used for a longer period of time. If you T-fans want to know more about the TBW formula, I have sorted it out for you!
 P/E Cycle (Program Erase Cycle)
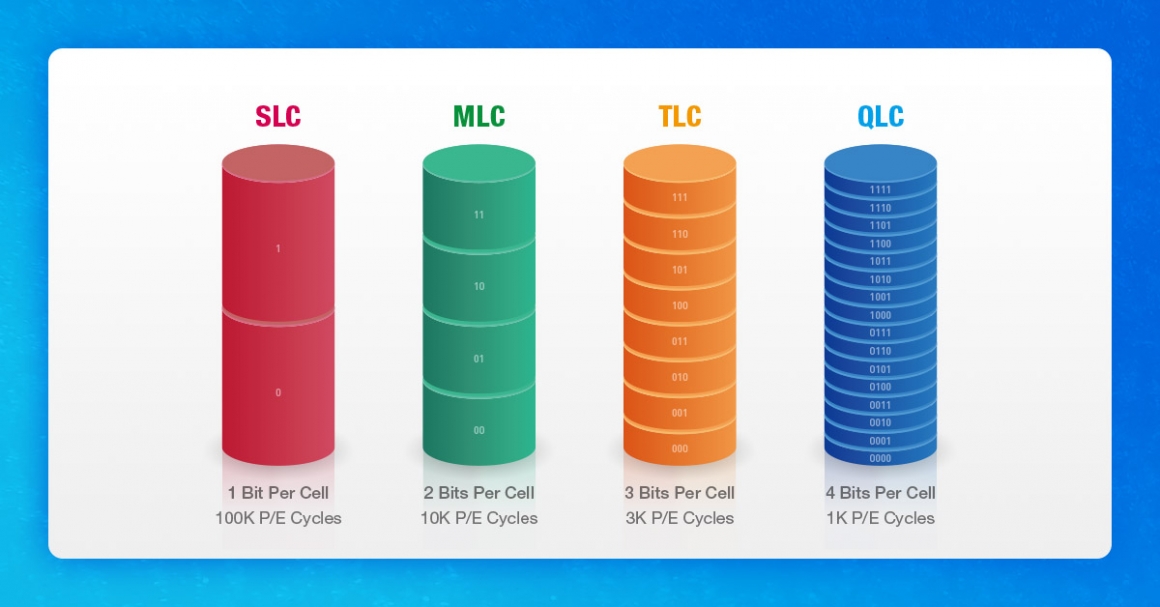
P/E Cycle (Program Erase Cycle) is the number of times the NAND can be erased and written. 1 write and 1 erase is 1 P/E Cycle. Theoretically, the P/E Cycle of SLC is 100,000 times, MLC is 5,000~10,000 times, and TLC is 1,000 times. The number of times here does not mean that the SSD will be broken after 1,000 reads and writes, but represents the number of cycles that each single storage block can be erased and written. Therefore, for the same SSD item, the P/E Cycle of different capacities will be the same!
 Write Amplification Factor (WAF)
Write Amplification Factor (WAF) is the ratio of the amount of data actually written to the SSD to the amount of data that the host request to be written at one time. I know it’s very complicated, you don’t have to memorize it, because the value of WAF will be different due to the manufacturing process of SSD controller, so you won’t actually know this value from the general SSD specification sheet. Just know that when calculating TBW, we will set the same SSD items to the same value to facilitate the calculation.
3. SLC Cache
The SLC Cache is a space divided in the NAND flash of the SSD that is used as a buffer area to simulate the SLC writing method in order to achieve “accelerated” access. As mentioned, we divide some space for cache use. If the cache space reaches the limit, the read and write speed will drop back to the original access speed of the NAND Flash in the SSD.
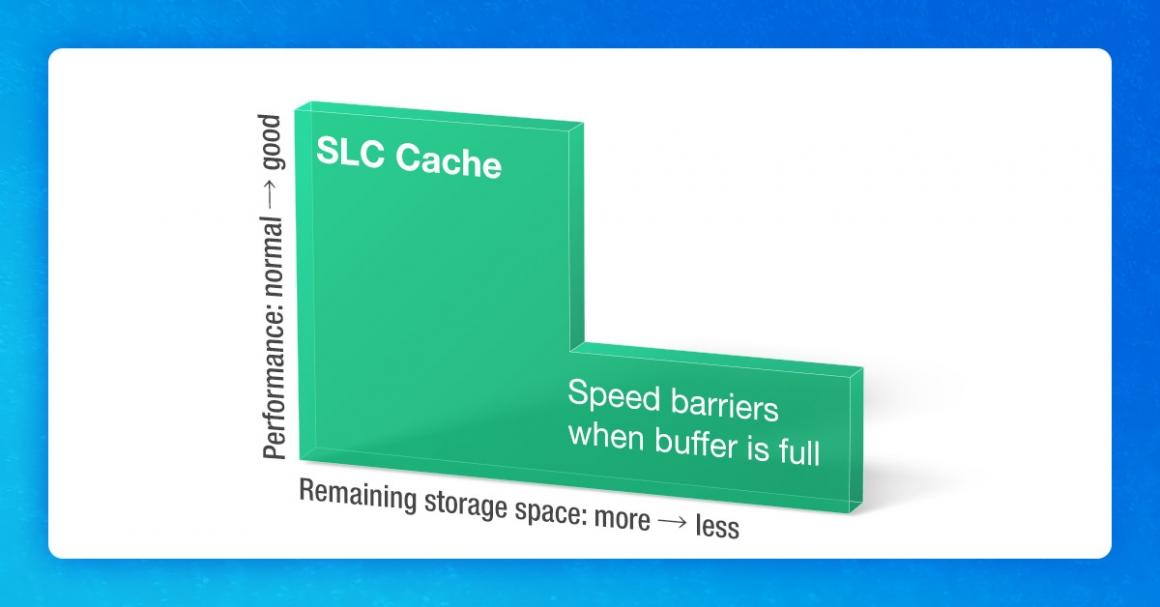
SSDs on the market will use around 30% of the storage space as the dynamic SLC Cache space. The larger your SSD capacity, the more SLC cache space you will have for higher speed performance. For example, a 2TB SSD will have about 600GB of SLC Cache.
~T-Tips~
I recommend all T-fans store the operating system separately from the common operating software and the output files. Keep the storage space on the SSD where the operating software is stored below 30% of the total capacity, so that the SSD can maintain high-speed transfer performance!
Conclusion
I guess all you T-fans are having headaches right now, let me summarize them for you!
When you want to upgrade your SSD, a high-capacity SSD will not only offer an upgrade in storage space, but will also provide better performance in terms of service lifetime and storage performance:
I. Large capacity SSD has more blocks that can be written and erased, and the application of Wear Leveling improves the durability and service life of SSD.
II. Large capacity SSD has a larger TBW value and the total amount of data that can be written is larger, which indirectly means that the SSD has a longer service life.
III. High-capacity SSD has a larger proportion of dynamic SLC Cache space, which can maintain high-speed transfer performance for a longer period of time.
If you want to learn more or have a topic that you want to know more about, please leave a message to let me know! If you like this article, remember to share and hit the like button. We’ll see you T-fans again next time!





